Global Weather Disruptions: the Aftermath of Tonga’s Volcanic Eruption
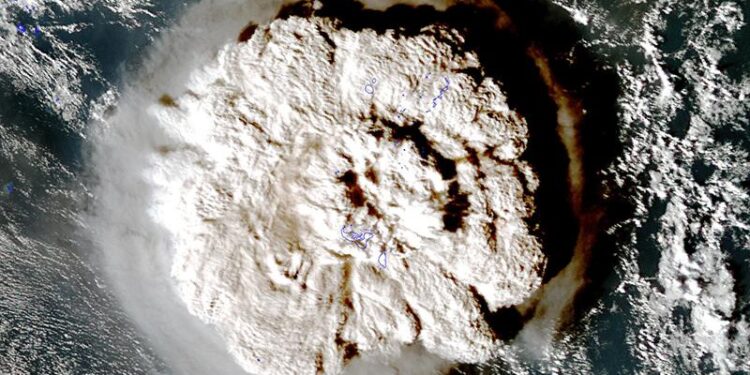
A recent examination by scientists at ‚Ā§UNSW Sydney has unveiled‚Ā£ that the devastating volcanic eruption in Tonga earlier this year ‚Äćmay have notable‚Ā§ repercussions for global weather systems, perhaps affecting climatic conditions‚ÄĆ throughout the decade. As ash‚Äć and ‚Äčgases from the eruption continue to permeate the atmosphere, experts caution that ‚Ā§we coudl be on the verge of experiencing remarkable weather phenomena, including ‚Ā§ shifts in precipitation patterns and heightened storm activity. This pivotal research highlights the intricate ‚ĀĘrelationships between volcanic eruptions and climate dynamics,urging governments‚Äč and communities to brace for a future where unusual weather occurrences may become commonplace.
Tonga‚Äôs Eruption: A Catalyst for‚ÄĆ Global Atmospheric‚ĀĘ Changes
The recent volcanic activity in Tonga has released substantial quantities of ash and water vapor into the atmosphere,‚ÄĆ raising alarms among researchers about its potential to‚Äč disrupt ‚Äćglobal weather patterns. ‚ĀĘFindings from UNSW Sydney indicate that these atmospheric alterations could linger well into subsequent years, resulting in‚ĀĘ unprecedented climatic shifts. Key potential outcomes identified include:
- Increased Rainfall: Areas typically known for arid conditions might see a surge in precipitation.
- Temperature Variability: Changes in atmospheric composition could lead to unexpected seasonal temperature variations.
- Agricultural Disruptions: Farmers may encounter challenges with planting and harvesting timelines, impacting food supply chains worldwide.
this‚Ā£ eruption’s impact on stratospheric conditions could also influence climate systems ‚Äćresponsible for regulating weather. The study elaborates on how volcanic particles ‚ĀĘcan serve as ‚ĀĘreflective shields against sunlight, inducing cooling effects in certain regions while possibly promoting warming trends elsewhere. The table below outlines projected regional weather implications:
| Region | plausible Weather‚ÄĆ Impact | Expected Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Northern America | An uptick in storm frequency | 5-10 years |
| Pacific Asia Region | An increase ‚Ā£in humidity and rainfall ‚Äćlevels | >3-7 years |
Deciphering Climate Patterns: The Influence of‚Äć Tonga‚Äôs Volcanic Activity on ‚Ā§Global Weather Systems
Tonga is located within a region ‚Ā§prone to significant volcanic events that‚ÄĆ have consequences extending far beyond its borders. Recent studies from UNSW Sydney suggest that such eruptions can‚Ā£ modify ‚Ā£atmospheric conditions considerably enough to reshape global‚Ā§ climate trends. The emission of ash and gases‚ÄĒparticularly sulfur dioxide‚ÄĒcontributes to sulfate aerosol‚Ā§ formation which can induce atemporary cooling affect in our ‚ĀĘatmosphere.This natural occurrence can disrupt established weather patterns and potentially affect precipitation rates, ‚Äčwind currents, and also ocean temperatures over extended periods.
Experts have identified several critical ways through which eruptions from Tonga might influence global meteorological systems:
- < strong>cooling Temperatures‚Ā£ : Elevated aerosol concentrations can reflect solar radiation leading to decreased‚ĀĘ surface temperatures .< / li >
- < strong>Diverse Rainfall Patterns : Alterations ‚ÄĆwithin atmospheric circulation might result in unforeseen droughts or flooding across various locales .< / li >
- < strong>Sporadic Weather Extremes : Projections indicate an increased likelihood of extreme meteorological events ,such as storms .< / a >
< / ul >Impact Potential Outcomes
Cooling Effect A‚Ā§ temporary reduction globally temperature wise during ‚Äćshort term .< / td > Divergence In Rainfall .< td /> Droughts or heavy rainfalls regionally.< / td >< < The Frequency of ‚ÄčStorms .< td /> An increase storms , with possibilities severe adverse‚Äč weathers.< / td > Strategies for Adapting to Emerging Weather Realities Ahead¬†¬†
The fallout from Tonga‚Äôs explosive eruption goes beyond immediate environmental changes; it compels communities worldwide reevaluate their strategies regarding impending meteorological challenges effectively adapting ‚Ā§requires ‚Äčauthorities individuals alike adopting proactive measures towards preparedness concerning unpredictable climates‚Äč investing advanced forecasting technologies utilizing cutting-edge models ensuring greater accuracy predicting atypical climatic behaviors ‚ĀĘkey recommendations adaptation encompass:< p/>
- <
- < strong>Bolstering Infrastructure :   ; Invest durable materials designs‚Äć withstand extreme environmental impacts.< / li >  ;
- < strong>Evolving Emergency Response ‚ÄćProtocols :   ; Regularly‚Äć update test evacuation plans ensure community readiness.< / li >  ;
- < strong>Cultivating public Awareness :   ; Launch educational initiatives surrounding resilience personal protective strategies.< / li >  ;
& lt;/ ul><
Furthermore engaging local populations adaptation processes ‚Äčessential fostering resilience achieved‚ĀĘ collaborative efforts focusing sustainable practices conservation initiatives establishing green spaces restoring natural habitats crucial‚Ā§ mitigating adverse effects climate upheaval straightforward approaches community engagement include:< p/>
< strongly>< Initiative >< < Description >
& lt;/ tr >/thead< Community Workshops >> < Interactive sessions teaching sustainability ‚Äćresilience techniques.& gt;< / ‚Ā£ ‚Ā£ ¬† ¬† ‚Ä欆 ¬† ¬† ¬† ‚Ä欆 ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ‚Ā£ ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ‚Äč ¬†¬† ‚Ā£ ¬†¬† ¬†¬† ¬†¬†