Unveiling the Depths: Exploring the Mariana Trench – The Deepest Point on Earth
In the unfathomable depths of the Pacific Ocean lies one of the most mysterious and awe-inspiring natural wonders on our planet: the Mariana Trench. Stretching over 1,550 miles and reaching a staggering depth of approximately 36,000 feet, this underwater abyss has captivated scientists and explorers for decades. Located east of the Mariana Islands, the trench is not only a geographical marvel but also a vital area for understanding oceanic processes and the life forms that thrive in some of the planet’s most extreme conditions. In this article,we delve into the captivating world of the Mariana Trench,unpacking its location,exploring remarkable facts,and offering a glimpse of the latest maps and images that highlight this deep-sea phenomenon-shedding light on what lies beneath the waves and why it matters for our understanding of Earth’s ecosystems.
Exploring the Depths of the Mariana Trench: A Comprehensive Overview
The Mariana Trench, located in the western Pacific Ocean, is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth, reaching an astonishing depth of approximately 36,000 feet (10,973 meters).This remarkable underwater feature, formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the Mariana Plate, offers a unique glimpse into one of the planet’s most uncharted territories. Scientists and explorers are continuously drawn to this abyss, not just for its extreme depths but also for the unusual and mysterious life forms that inhabit its dark waters. Notable expeditions have unveiled a plethora of new species, demonstrating that life thrives in even the most unfriendly environments.
Several notable facts about this intriguing marine landscape include:
- Location: Coordinates are approximately 11°21′ North, 142°36′ East.
- Dimensions: About 1,550 miles (2,500 kilometers) long and varying in width.
- Exploration Milestones: First visited by humans in 1960,and more recently explored using advanced submersibles.
This trench plays a crucial role in global oceanographic processes and is a key focal point for researchers aiming to understand plate tectonics, marine biology, and the effects of climate change on ocean ecosystems. A recent research initiative is utilizing technological advancements, such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), to map and study the trench with unprecedented detail.
Unraveling the Mysteries: Key Facts and Geographic Insights
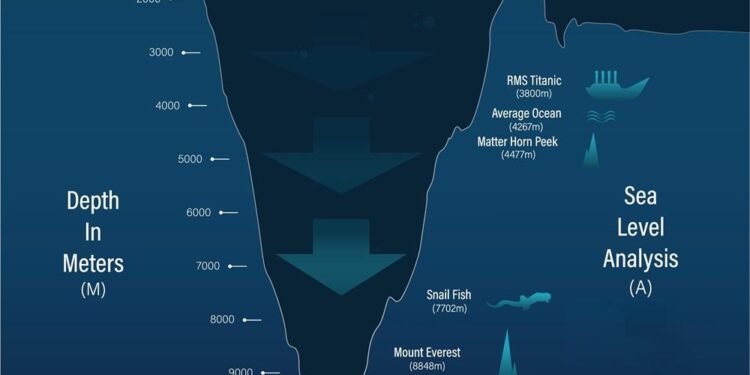
The Mariana Trench,the deepest oceanic trench in the world,plunges to a staggering depth of approximately 36,000 feet (10,973 meters). Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Mariana Islands. This unique geographical feature not only challenges our understanding of marine ecosystems but also offers a glimpse into the planet’s geological past. The trench spans about 1,550 miles (2,500 kilometers) in length and reaches widths of up to 43 miles (69 kilometers) at certain points, making it a foundational component of deep-sea research.
Exploration of the Mariana Trench has revealed several astonishing facts.As a notable example, the extreme pressure at the bottom-around 1,000 times that of standard atmospheric pressure-creates an habitat unlike any on Earth’s surface. The trench is home to various unique organisms, including the resilient amphipod known as the “deep-sea snailfish,” which has adapted to thrive in such harsh conditions.Researchers have also estimated that there are over 200,000 undiscovered species residing in the trench, emphasizing the importance of continued exploration and study. The following table provides a concise overview of notable aspects of the Mariana Trench:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Depth | 36,000 feet (10,973 meters) |
| Location | Western Pacific Ocean |
| Length | 1,550 miles (2,500 kilometers) |
| Species Diversity | Estimated 200,000 undiscovered species |
Visual Journey: Maps and Stunning Images of the Deepest Oceanic Trench
Embarking on an exploration of the Mariana Trench transports us into a realm where light retreats, and the mysteries of the deep ocean unfold. The trench, located in the western Pacific Ocean, reaches a staggering depth of 36,000 feet (approximately 10,900 meters), making it the deepest known part of the Earth’s oceans. Positioned east of the Mariana Islands, this geological wonder is not only a testament to the Earth’s tectonic activity but also a breathtaking canvas for cutting-edge maps and striking imagery that capture its elusive beauty. Through high-resolution sonar technology and remotely operated vehicles, scientists have begun to chart these depths, revealing a world teeming with unique ecosystems and vibrant, bioluminescent creatures.
Accompanying this exploration are stunning visuals that highlight the trench’s dramatic landscapes. Here are some fascinating elements that have been captured:
- Underwater Volcanoes – Towering structures that spew mineral-rich materials.
- Submarine Canyons – Steep sides carved by ancient currents, creating a striking contrast in the seafloor.
- Strange Marine Life – Organisms such as the amphipod and the snailfish that thrive in extreme conditions.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean, east of the Mariana Islands |
| Maximum Depth | 36,000 feet (10,900 meters) |
| Key Residents | Amphipods, Deep-sea Cusk Eels, Sea Cucumbers |
To Wrap It Up
the Mariana Trench stands as a testament to the wonders and mysteries of our planet’s oceanic depths.With its staggering depth of over 36,000 feet, the trench not only captures the imagination of scientists and explorers alike but also serves as a crucial area for studying the complexities of marine life and geological processes. Through advances in technology and exploration, our understanding of this unique environment continues to evolve, revealing new insights into the Earth’s diverse ecosystems. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the Mariana Trench, we must also remain committed to its preservation, ensuring that this extraordinary part of our world is protected for future generations. For more in-depth data,maps,and stunning images,be sure to explore the full article on Britannica.