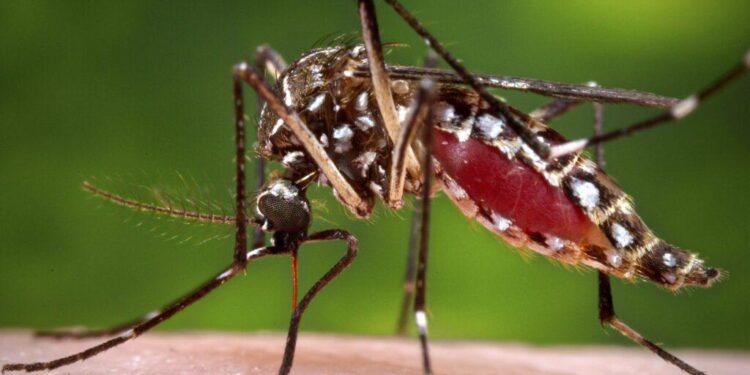
Discovering Cold-Resilient Mosquitoes in Iceland: A New Chapter in Adaptation
In a remarkable discovery that could reshape our understanding of mosquito adaptability, researchers have identified a unique population of cold-resistant mosquitoes thriving in the frigid landscapes of Iceland. This pivotal finding, brought to light by scientists studying the local insect ecosystem, raises intriguing questions about these insects’ survival capabilities in extreme climates. Traditionally associated with warmer regions, this newly discovered species demonstrates an extraordinary ability to thrive under conditions previously thought uninhabitable. As climate change continues to alter habitats worldwide, the implications of this discovery may reach far beyond Iceland’s shores, affecting ecosystems and public health globally. The Reykjavik Grapevine delves into the significance of this finding and its potential consequences while exploring ongoing research aimed at uncovering the secrets behind these resilient mosquitoes.
Cold-Resistant Mosquitoes Discovered in Iceland: An Evolutionary Breakthrough
Surprisingly, scientists have found a new species of mosquitoes capable of surviving Iceland’s notoriously low temperatures. These cold-resistant mosquitoes challenge long-standing assumptions about insect adaptability limits within extreme environments. Field studies conducted across various locations in Iceland reveal that these insects can flourish even amidst sub-zero temperatures-a remarkable evolutionary feat. They possess distinct physiological adaptations that allow them to enter dormancy during harsh conditions, effectively pausing their metabolic processes until warmer weather returns.
The ramifications stemming from this discovery are significant for both biodiversity and climate change research alike. As unpredictable weather patterns become more common due to global warming, understanding how various species adapt is crucial for future ecological stability. Key factors contributing to the resilience exhibited by these cold-tolerant mosquitoes include:
- Antifreeze proteins: Enabling survival under freezing conditions.
- Dormancy behavior: Allowing them to withstand severe winters.
- Accelerated reproduction rates: Enhancing their chances as environmental conditions fluctuate.
This breakthrough not only sheds light on life’s complexities within extreme climates but also raises questions about how such species might expand their territories as global temperatures rise.
Consequences for Ecosystems and Public Health Due to Cold-Tolerant Mosquitoes
The emergence of cold-adaptive mosquitoes presents significant challenges for both local ecosystems and public health systems in cooler regions like Iceland’s environment. Historically inhospitable areas have limited mosquito populations; however, with this newly adapted species now present, concerns arise regarding potential disruptions to established ecological balances and new health threats . Important considerations include:
- Biodiversity Impact: The introduction of cold-resistant mosquitoes may threaten native insect populations leading to shifts within existing predator-prey dynamics.
- Disease Transmission Risks: With adaptation comes an increased likelihood that diseases such as West Nile virus or Zika virus could spread into previously unaffected areas.
- Pandemic Preparedness Measures: Health authorities must reevaluate current strategies concerning potential outbreaks linked with these new mosquito populations.
The interactions between these hardy insects and local wildlife could yield unforeseen consequences; if birds or bats begin preying on them more frequently than other available food sources-this shift has implications for overall population dynamics within those ecosystems requiring careful monitoring.
| Ecosystem Effects | Pertinent Public Health Concerns |
|---|
Approaches for Managing Mosquito Populations in Unlikely Habitats
Tackling mosquito management challenges posed by unexpected habitats like those found throughout Iceland necessitates innovative strategies-especially given the rise of cold-adaptive varieties among them! One effective method involves enhancing environmental surveillance systems specifically designed around tracking where exactly these resilient pests thrive best using advanced technologies such as remote sensing combined with geographic information systems (GIS). Additionally establishing community reporting networks empowers residents themselves-allowing individuals living nearby unusual activity report findings which contribute towards collaborative efforts aimed at monitoring trends over time.
An alternative strategy includes implementing targeted larvicides focused upon breeding grounds identified through previous assessments made possible via enhanced monitoring techniques mentioned earlier! Recent investigations indicate natural control methods-including introducing predators alongside utilizing essential oils-can prove beneficial without adversely affecting other non-targeted organisms present nearby too! Furthermore launching educational campaigns geared towards raising awareness surrounding minimizing standing water accumulation around homes/outdoor spaces will help mitigate risks associated directly related back again towards increasing numbers seen lately amongst certain types found locally too!
Looking Forward: Addressing New Challenges Posed By Cold-Tolerant Mosquitos In Icelands Unique Ecosystems!
In conclusion-the identification/discovery surrounding newfound populations exhibiting traits allowing survival despite harsh climatic extremes represents pivotal advancements made recently concerning our understanding regarding insect adaptability/resilience against changing environments brought forth largely due primarily because climate change continues impacting all aspects life today including biodiversity conservation efforts moving forward into future generations ahead still yet unknown outcomes await us all involved closely watching developments unfold further down road ahead together collaboratively working toward solutions necessary ensuring balance maintained throughout entire ecosystem intact while safeguarding human health simultaneously too!