Impending Disruption of Ocean Currents: A Looming Danger for Northern Europe’s Climate
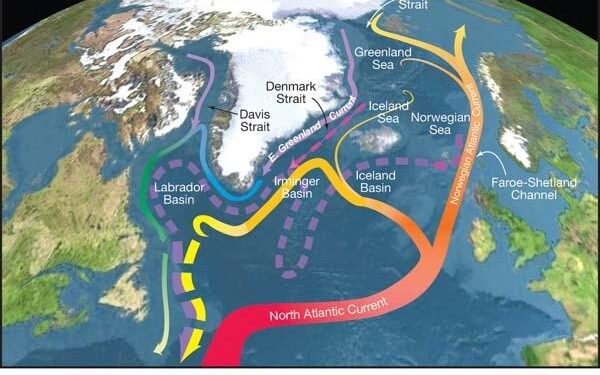
Recent climate research has brought to light a troubling scenario: the potential breakdown of ocean currents could lead to significant cooling in Northern Europe, counteracting the overarching trend of global warming. This study highlights that disturbances in essential oceanic systems, particularly the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), may not only exacerbate regional weather irregularities but also alter Europe’s climatic landscape. This creates a perplexing situation where rising global temperatures coincide with localized cooling effects. As scientists delve deeper into these implications, it becomes increasingly critical to understand and address the complex interplay between ocean currents and climate change. This article explores the possible repercussions of such disruptions and their effects on millions living in impacted regions.
Understanding Ocean Current Disruptions and Their Implications for Northern Europe
Recent studies have illustrated how interruptions in ocean currents, especially those related to AMOC, can significantly alter climate patterns, resulting in marked cooling effects across areas like Northern Europe. These changes are primarily driven by melting ice sheets and rising sea temperatures that modify seawater salinity and density-key elements influencing ocean circulation dynamics.The decline of these currents could trigger a cascade of climatic shifts including:
- Increased sea-level rise: Heightened coastal flooding and erosion may threaten infrastructure and also ecosystems.
- Altered weather patterns: Changes in precipitation rates and storm severity could disrupt agriculture and water availability.
- Biodiversity challenges: Shifts within marine ecosystems might jeopardize fishing industries and food security.
The consequences of a potential collapse extend beyond mere temperature changes. Climate specialists warn about unforeseen outcomes accompanying such shifts that could lead to abrupt regional cooling even while global temperatures continue to rise. Alterations within oceanic circulation might lock Northern Europe into prolonged cold spells, impacting seasonal cycles as well as agricultural productivity.Given the interconnected nature of global weather systems, localized changes can resonate worldwide; thus international collaboration is vital for effective climate mitigation strategies. Key considerations include:
- Investment in research: Increased funding for climate science is essential for improved forecasting capabilities regarding future changes.
- Crisis management policies: Comprehensive strategies aimed at reducing emissions alongside conservation efforts are crucial for stabilizing climatic systems.
- Civic resilience planning: Preparing communities for potential disruptions through educational initiatives and infrastructure improvements is imperative.
Impact of Cooling Trends Within a Warming Climate
The intricate relationship between ocean currents and climate stability has gained considerable attention as evidence mounts suggesting that disruptions may result in severe regional cooling-especially across Northern Europe. While average global temperatures continue their upward trend due to warming influences, there exists an alarming possibility that sudden collapses within these current systems could lead to sharply declining local temperatures-a phenomenon contradicting overall trends associated with climate change. Noteworthy consequences include:
- Diverse weather pattern alterations: Changes within ocean flows can produce erratic weather conditions characterized by heavy snowfall or unseasonal frosts.
- Agricultural difficulties:A cooler environment may shorten growing seasons adversely affecting crop yields along with food security concerns.
< li >< strong >Economic ramifications:< / strong > Industries reliant on stable climates-including agriculture tourism-may encounter unexpected challenges due unpredictable conditions.< / li >
The cascading impacts arising from such cooling events highlight the complexities associated with regional manifestations of climate change . To clarify this phenomenon further , consider this table summarizing possible impacts based on varying degrees temperature decline :
Cooling Degree Potential Consequence 1-2¬įC Increased autumn frost , early snowfalls . 3-4¬įC Severe winter storms ,crop failures . 5¬įC + < td >Major economic disruption , loss agricultural biodiversity . Policy Strategies for Adapting to Altered Ocean Currents
Acknowledging recent findings indicating potential failures among key ocean current systems-and their subsequent repercussions on global climatic patterns-policymakers must act decisively with strategic measures aimed at mitigating risks linked with drastic temperature drops across northern European regions.< strong >Adaptive approaches< / strong > should prioritize enhancing resilience through improved infrastructure alongside sustainable urban development initiatives. Essential actions encompass :
- < li >< strong >Investments Renewable Energy :< / strong  Transition towards wind ,solar ,tidal energy sources reduces dependence fossil fuels while curbing greenhouse gas emissions .< / li >< li >< strong  Strengthening Coastal Defenses :< / strong  Implement flood barriers natural defenses like restoring mangroves protect residential agricultural zones from extreme meteorological events.< / li >< li >< strong  Regional Climate Monitoring :< / strong Establish advanced analytics track shifts occurring within marine environments enabling timely responses emerging threats.< / li >< li />
Furthermore promoting public awareness community engagement remains critical fostering collective responses addressing impending environmental challenges Local governments should develop educational programs inform citizens regarding consequences altered marine flows effective preparedness measures Initiatives might involve :
Policy Area Proposed Initiative Expected Outcome
/ tr /
/ Thead /Reduced carbon footprint.
/ Td /
/ Tr /Minimized flood risk.
/ Td /
/ Tr /Informed communities.
/ Td /
/ Tr /Conclusion: Outlook on Future Consequences
The imminent threat posed by failing ocean currents signifies a serious concern regarding northern Europe’s future stability As ongoing investigations reveal complexities surrounding interactions between these vital waterways warming atmosphere implications resulting from their disruption could lead unexpected shifts including pronounced drops already vulnerable areas facing adverse effects related changing climates Policymakers scientists alike must heed warnings prioritize robust adaptation mitigation frameworks Findings highlight urgent necessity further exploration aquatic ecosystems as health integral not just marine environments but also overall planetary equilibrium As we confront realities rising heat levels evident oceans frequently enough viewed distant entities hold crucial insights determining fate our world .