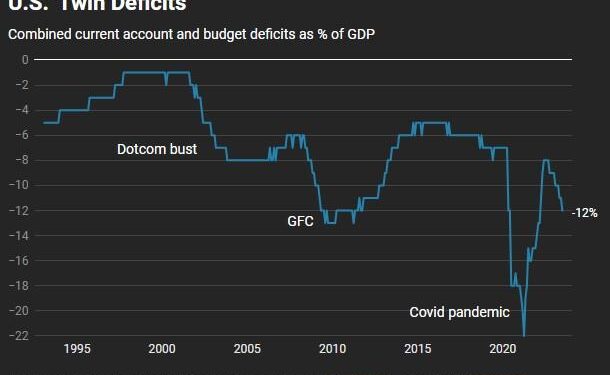
In recent years, the economic landscape of the United States has been increasingly characterized by a phenomenon known as the “twin deficit trap.” This term refers to the simultaneous occurrence of a fiscal deficit, wherein government expenditures outpace revenues, and a current account deficit, which reflects a shortfall in national savings relative to investment. As policymakers grapple with these intertwined challenges, the implications for economic growth, currency stability, and international trade become ever more pronounced. In this article, we will delve into the root causes and potential consequences of America’s twin deficit trap, examining how it shapes the financial future of the nation and what strategies could be employed to mitigate its effects. From the impact of rising national debt to the vulnerabilities it creates in global markets, understanding this crucial economic issue is essential for grasping the complexities of America’s fiscal health and the potential paths forward.
Understanding the Implications of America’s Twin Deficit Trap
The concept of America’s twin deficit trap refers to the dual issues of a persistent fiscal deficit and a burgeoning current account deficit.These two deficits are interlinked,creating a feedback loop that complicates economic policy and risks long-term stability.When the government spends more than it earns, it leads to increased borrowing, which can result in elevated interest rates. Consequently, higher interest rates may attract foreign capital to fund the fiscal shortfall but concurrently strengthen the dollar, making U.S. exports less competitive on the global market. This phenomenon exacerbates the current account deficit by increasing imports while suppressing exports, challenging economic resilience.
Addressing this duality requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Fiscal Discipline: Implementing policies to reduce government spending or enhance revenue streams to mitigate fiscal deficits.
- Trade Policies: Exploring diplomatic avenues to bolster export growth while managing import levels.
- Investment in Innovation: Fostering sectors capable of generating trade surpluses and competitive advantages.
To illustrate the potential outcomes of this predicament, consider the following table that summarizes the key economic indicators affected by the twin deficits:
| Indicator | Current Status | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Fiscal Deficit (% of GDP) | ~6.5% | Increased borrowing costs |
| Current Account Deficit (% of GDP) | ~3.5% | Depressed export performance |
| Interest Rates | 4.5% | Potential capital flight |
Evaluating the Economic Drivers Behind the Twin Deficits
The economic landscape of the United States is increasingly characterized by the phenomenon of twin deficits – a simultaneous occurrence of a budget deficit and a current account deficit. These two deficits can be heavily intertwined, creating a complex web of economic challenges. Several key factors drive this situation, including:
- Increased Government Spending: The rise in federal spending, often intended to stimulate economic growth, can lead to higher budget deficits.
- Trade Imbalances: A lack of competitiveness in global markets can result in a higher current account deficit as the country imports more than it exports.
- Low Savings Rates: Consumer behavior reflects a low personal saving rate, further exacerbating the demand for foreign capital.
The implications of this financial scenario are profound. An understanding of these drivers is essential for formulating effective policies. Some of the economic effects can include:
| Economic Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Currency Depreciation | A rising deficit often leads to a weaker dollar, increasing import costs. |
| Interest Rate Fluctuations | Higher government borrowing could increase interest rates to attract foreign investors. |
| Future Economic Growth | Persistent deficits may hinder lasting growth, affecting long-term investment strategies. |
Strategic Recommendations for Mitigating Financial Risks
To effectively address the escalating financial risks associated with America’s twin deficits, stakeholders should focus on integrating a multifaceted approach that emphasizes fiscal obligation and economic resilience. Key strategies include enhancing budgetary discipline by curtailing non-essential government expenditures, which can, in turn, help stabilize the national debt. Additionally, implementing dynamic tax reforms aimed at broadening the tax base will ensure a more equitable distribution of fiscal responsibility while generating revenue to tackle deficits without imposing undue burden on any single demographic group.
Moreover, fostering sustainable economic growth through targeted investments in technology and infrastructure can reduce reliance on foreign goods, thereby curbing trade deficits. Encouraging innovation via public-private partnerships will further stimulate job creation and improve productivity across industries. Lastly, establishing clear monetary policies that prioritize interest rate stability can help manage inflationary pressures linked to increased borrowing. By adopting these strategies, the likelihood of severe economic repercussions stemming from persistent deficits can be significantly diminished.
In Summary
America’s twin deficit trap represents a complex interplay of fiscal and trade challenges that threaten the nation’s economic resilience. As the government grapples with mounting budget deficits alongside a persistent trade imbalance, understanding the implications of this dual predicament is crucial for policymakers, investors, and citizens alike. The potential consequences of sustained deficits-ranging from weakened dollar valuation to increased borrowing costs-underscore the urgent need for strategic reforms aimed at fostering fiscal discipline and promoting export growth. As the U.S. navigates its path forward, the decisions made today will reverberate through its economic landscape for years to come. Addressing these intertwined issues will be essential not only for stabilizing the economy but also for ensuring long-term prosperity. Keeping a vigilant eye on these developments will be imperative for stakeholders across the board as they seek to adapt in an evolving global marketplace.