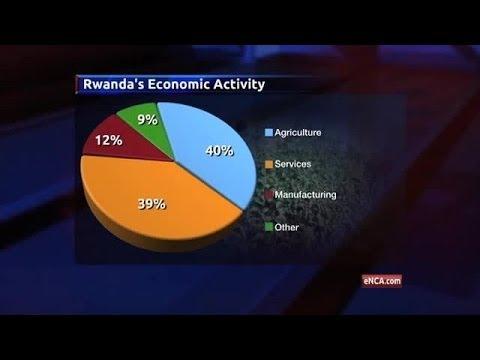
Rwanda’s economy is projected to experience a deceleration in growth in 2025, according to recent statements from the nation’s finance minister. This forecast comes amid a global economic landscape marked by uncertainty, rising inflation, and shifting trade dynamics. While Rwanda has been recognized for its notable recovery and resilience post-genocide and for maintaining relatively strong growth rates in recent years, this latest outlook signals potential challenges ahead. As the government prepares to navigate this anticipated slowdown, stakeholders are keenly observing how policymakers will adapt their strategies to ensure lasting advancement and economic stability in the years to come.
Rwanda’s Economic Growth Forecast Faces Challenges Amid Global Uncertainties
Rwanda’s economic outlook for 2025 is becoming increasingly complex as the nation grapples with various external challenges that threaten its growth trajectory. According to the Minister of Finance, these challenges stem primarily from global economic uncertainties, including fluctuating commodity prices, supply chain disruptions, and inflationary pressures. As the international landscape shifts, Rwanda’s ability to maintain its impressive growth rate, which was bolstered by post-pandemic recovery efforts, is now under scrutiny.
In light of these developments, several key factors are expected to influence Rwanda’s economic performance in the coming years:
- Export Vulnerability: The nation relies heavily on exports, especially in agriculture and minerals, making it susceptible to global market volatility.
- Investment Climate: Foreign direct investment may decline if investors perceive heightened risks associated with global uncertainties.
- Inflation Impact: Rising prices of essential goods could reduce consumer spending and overall economic activity.
| Economic Indicator | 2023 Estimate | 2025 Forecast |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate (%) | 8.5 | 5.2 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 7.0 | 6.5 |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 2.0 | 2.8 |
Understanding these trends is critical, as they will not only affect Rwanda’s internal development plans but also its position in the regional and global economic landscape. Strategic adjustments are vital for mitigating risks and ensuring resilience against external shocks, enabling Rwanda to navigate through these uncertain times effectively.
Insights into Key Sectors Impacted by Slowing Growth Trends
The anticipated slowdown in Rwanda’s economic growth is set to ripple through several key sectors, each facing unique challenges and adaptations in response to the evolving landscape. The agriculture sector, which has long been the backbone of the Rwandan economy, is grappling with the impacts of climate change and market access issues. Farmers may find it increasingly arduous to sustain productivity levels, leading to concerns about food security and export revenues. Similarly, the manufacturing sector may experience a reduction in demand due to lower consumer spending, resulting in potential layoffs and stunted growth for SMEs.These sectors will require strategic pivots to navigate slower growth dynamics effectively.
Another area facing critically important pressure is tourism, which has been a vital contributor to Rwanda’s GDP. The slowdown might deter international travel and reduce the influx of foreign visitors, impacting both major hotel chains and local tour operators. Moreover, the technology sector, while still on an upward trajectory, could see investment funding tighten, forcing startups to rethink their growth models and operational strategies. To illustrate the emerging trends across these sectors in light of the projected growth deceleration, consider the following table summarizing the anticipated impacts:
| Sector | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Reduced productivity and potential food security risks |
| Manufacturing | Decreased consumer demand leading to layoffs |
| Tourism | Lower international arrivals affecting revenue |
| Technology | Investment constraints impacting startup growth |
Strategic Recommendations for Sustainable Economic Resilience and Diversification
To navigate the anticipated slowdown in economic growth, it is essential for Rwanda to embrace a series of strategic initiatives aimed at fostering resilience and diversification. Strengthening local industries should be prioritized to reduce dependency on imports and enhance self-sufficiency. This includes investments in technology and training programs to boost productivity in sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and services. Key strategies may include:
- Enhancing access to financing for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
- Promoting sustainable agricultural practices to increase food security
- Encouraging innovation through research and development grants
Another critical area for development is the expansion of Rwanda’s export markets.By diversifying trade partnerships and enhancing the quality of exportable goods, the country can mitigate risks associated with fluctuating global demand. Collaborative efforts should seek to improve infrastructure and logistics, facilitating smoother trade operations. The implementation of trade agreements with regional and international partners could also serve to deepen economic ties. A summary of potential focus areas for diversification can be laid out as follows:
| Focus Area | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Technology in Agriculture | Increased productivity and sustainability |
| Investment in Manufacturing | Reduced import reliance |
| Regional Trade Partnerships | Diverse export markets |
To Wrap It Up
while Rwanda’s economy has shown resilience and a commendable growth trajectory in recent years, the forecasted slowdown in 2025 signals a need for cautious optimism and strategic planning. As articulated by the Finance Minister, the government must navigate a complex landscape of global economic pressures and domestic challenges. Stakeholders across sectors are urged to remain agile, embracing innovation and diversification to bolster economic stability. With continued focus on sustainable development and proactive policy measures, Rwanda can position itself to weather impending challenges while striving to achieve its long-term economic goals. As we monitor these developments, the implications for investment, employment, and overall economic health will be critical to watch in the coming months.