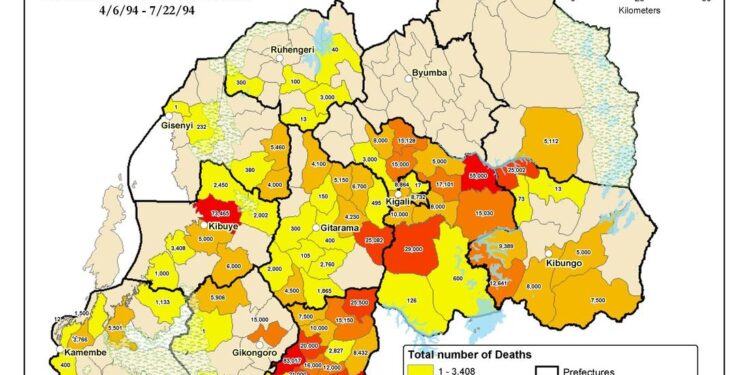
In a solemn reflection on one of the darkest chapters in recent history, the United Nations commemorates the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda, a systematic slaughter that resulted in the deaths of an estimated 800,000 people within just 100 days. As the international community grapples with the enduring consequences of this atrocity, UN officials reiterate the importance of remembrance and education to prevent such horrors from occurring in the future. This commemoration not only honors the memory of the victims but also highlights ongoing efforts to promote reconciliation, justice, and healing in a nation still grappling with the scars of its past. Through a series of events, discussions, and tributes, the UN seeks to foster a deeper understanding of the genocide’s causes and lessons, emphasizing the urgency of global vigilance against hate and violence.
UN Commemorates Rwanda’s 1994 Genocide While Pledging to Combat Future Atrocities
The United Nations marked the tragic anniversary of the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda, reflecting on the profound loss of life and the immeasurable suffering endured by countless families.In an emotional commemoration, UN officials emphasized the importance of remembering this dark chapter in history as a commitment to fostering a world where such horrors never occur again. The solemn observance included moments of silence, survivor testimonies, and a call for renewed vigilance against hate and intolerance. Key themes discussed included:
- Memory and Education: Emphasizing the need to educate future generations about the genocide.
- Prevention Strategies: Outlining actionable steps to identify and combat potential genocidal tendencies.
- Support for Survivors: Reiterating the commitment to providing ongoing aid and resources to genocide survivors.
Alongside remembrance, the UN pledged to enhance international collaboration in preventing future atrocities. Various initiatives were highlighted, promoting a multi-faceted approach that encompasses legal, diplomatic, and grassroots strategies. Collaborative efforts will focus on:
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Early Warning Systems | Develop mechanisms to detect signs of impending violence. |
| Community Engagement | Empower local voices to address tensions before they escalate. |
| International Cooperation | Strengthen partnerships across nations to ensure a unified response. |
Examining the Lessons Learned from the Rwandan Genocide on Global Human Rights
The Rwandan genocide serves as a harrowing reminder of the consequences of inaction in the face of escalating violence and human rights violations. In just 100 days, an estimated 800,000 Tutsis and moderate Hutus were brutally murdered, demonstrating the dark potential of ethnic hatred when left unchecked.The international community’s failure to intervene has led to critical reflections on several lessons that are now integral to discussions surrounding global human rights, including:
- The importance of early warning systems: Recognizing the signs of impending genocide is crucial. Implementing mechanisms to monitor and respond to rising tensions can save lives.
- The necessity for a unified global response: Fragmented actions can lead to delays that cost lives. A coordinated international approach is essential for effective intervention.
- The responsibility to protect (R2P): Nations must acknowledge their obligation to prevent mass atrocities, irrespective of borders, emphasizing a shift from sovereignty to accountability.
Furthermore, the aftermath of the genocide illustrates the need for comprehensive justice mechanisms and reconciliation processes. Post-genocide Rwanda has focused on national unity and healing, but the failure to adequately address the psychological scars remains an ongoing challenge. Essential strategies drawn from this experience include:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Truth Commissions | Facilitating open dialog about past atrocities to aid reconciliation. |
| Restorative Justice | Emphasizing healing and accountability rather than punishment alone. |
| Education and Awareness | Promoting human rights education to prevent future atrocities. |
Calls for Strengthened International Cooperation to Prevent Genocide and Protect Vulnerable Communities
The sobering reflections on the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda serve as a poignant reminder of the urgent need for enhanced international cooperation to prevent atrocities in vulnerable communities worldwide. As nations gather to remember the victims and analyze the failures of the past, it is crucial to emphasize collaborative mechanisms that promote early warning systems and effective intervention strategies. The global community must unite under shared principles aimed at safeguarding human rights, including:
- Strengthening diplomatic efforts to address ethnic tensions before they escalate
- Building robust international legal frameworks that hold perpetrators accountable
- Encouraging interdisciplinary partnerships between governments, NGOs, and civil society organizations
Moreover, the establishment of an inclusive dialogue encompassing marginalized groups is essential for fostering resilience against hate and discrimination. As we reflect on the past traumas, it is indeed imperative to also look ahead to actionable commitments that can empower local communities. A structured approach combining education, peacebuilding initiatives, and strategic partnerships will be instrumental in combatting the cycles of violence. The table below highlights key areas for collective action:
| Action Area | Objective |
|---|---|
| Prevention Education | Raise awareness about genocide prevention |
| Crisis Response Training | Prepare communities for rapid response during conflicts |
| Community Engagement | Develop inclusive initiatives that promote dialogue |
Key Takeaways
As the United Nations reflects on the tragic events of the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda, it is indeed crucial to remember not only the lives lost but also the resilience of the survivors who continue to bear the scars of this dark chapter in history. The UN’s renewed commitment to prevention, justice, and remembrance serves as a stark reminder that vigilance is essential in combating hatred and fostering peace worldwide. Through ongoing education and dialogue, the lessons learned from Rwanda must resonate far beyond its borders, urging global communities to confront and address the underlying issues of discrimination and intolerance. By honoring the memories of those affected, the international community can strive to ensure that such atrocities are never repeated, fostering a future rooted in understanding and respect for all humanity.