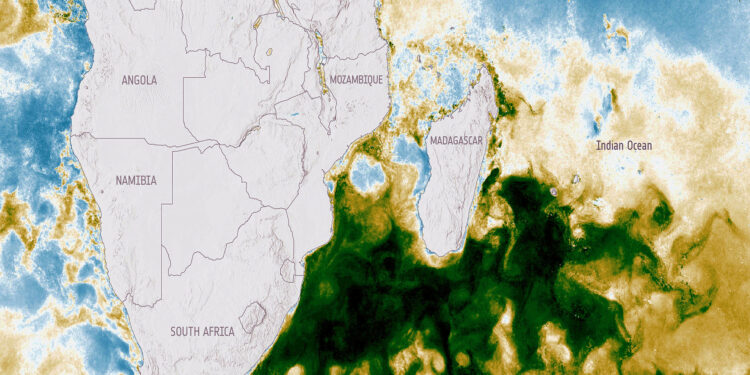
The Hidden Impact‚Äč of Dust: How Southern Africa’s Winds ‚ÄĆAffected Ocean ‚ÄčLife
Imagine, ‚Äćfor a moment, ‚ÄĆa gust ‚ÄĆfrom southern Africa stirring up minute particles ‚ĀĘof dust and casting them across the expansive Indian Ocean.‚Ā§ In 2019, this ‚ÄĆnatural phenomenon led‚Ā£ to‚ÄĆ astonishing consequences, triggering the most significant phytoplankton bloom seen in two decades ‚ĀĘduring a period‚Äč typically devoid of such ‚Äćactivity.
The Nutrient Journey ‚ÄĆof Dust
Often dismissed as an ‚ÄĆeveryday annoyance, dust harbors unforeseen‚ÄĆ benefits. These particulate clouds can travel vast distances‚ÄĒincluding over oceans. ‚Ā§A prime example‚Ā§ is the fine ‚ÄĆparticles from the Sahara Desert that make long journeys across ‚Ā§the ‚Ā§Atlantic to reach ‚ÄĆSouth America. When these tiny fragments settle on land or marine‚Ā§ environments, they provide ‚ĀĘcritical nutrients that promote vegetation growth on land and boost ocean productivity‚ÄĒserving as ‚Äča vital ‚ĀĘsource of nourishment for marine phytoplankton.
Exploring Connections Between Dust and Oceans
While it is acknowledged that dust‚Äč travels vast distances ‚ÄĆwith potential ecological impacts, the complex interrelations among desertification processes, dust dispersal events, and subsequent ocean fertilization remain ‚Ā£largely enigmatic. ‚Ā£Recent research published in PNAS Nexus adds‚Ā§ valuable insights to this intricate web.
An Uncommon Phytoplankton Bloom
A research team involving scientists from ESA‚Äôs Living Planet Fellowships Poseidon and Pyroplankton identified an extraordinary bloom off southern Africa‚Äôs eastern coastline. This event ‚ÄĆwas initiated by‚Äć what‚Äč is known as ‚Äúdust wet deposition‚ÄĚ‚ÄĒor rain ‚ÄĆthat ‚ĀĘcarries dust‚ÄĒoccurring in nutrient-poor waters located southeast of Madagascar. Spearheaded ‚Äćby Dr. John Gittings ‚ĀĘfrom the ‚ĀĘUniversity of Athens, this study significantly ‚Ā£advanced our understanding of this‚ÄĆ remarkable incident.
Tracing Dust’s Path to Marine‚Äč Environments
Utilizing ‚Äčdata gathered from multiple Earth‚ÄĆ observation programs spearheaded by ESA‚ÄĒincluding‚ÄĆ initiatives‚Ā§ focusing‚ĀĘ on ocean color ‚Ā§and soil moisture‚ÄĒthe‚Ā§ research team managed to delineate‚Ā§ the extent of this extensive phytoplankton bloom‚Ā§ while pinpointing specific dust events responsible for its occurrence. ‚ÄĆThis collaboration also involved contributions from services dedicated to ‚Ā§atmosphere monitoring and‚ĀĘ marine ‚ĀĘresearch within Europe‚Äôs Copernicus‚ĀĘ program.
Climate Change Implications: Increased‚ĀĘ Dust‚Äč Emissions?
Dr. ‚ÄĆGittings highlighted that while this expansive phytoplankton boom was atypical; trends‚Äč suggesting‚ÄĆ rising‚Äč temperatures alongside increasing aridity in southern Africa may indicate future occurrences could become ‚ĀĘmore frequent due to climate change factors ‚Äćlike increased droughts exacerbated by aerosols traced‚ÄĆ back ‚ĀĘto wildfire events elsewhere.
– How can ‚ÄĆsatellite data be used to study‚Äč phytoplankton trends?
How African Dust ‚Ā§Ignited a Thriving Phytoplankton Bloom: Nature’s Spectacular Chain‚Ā£ Reaction
Understanding ‚ÄĆthe Role of ‚Ā£African Dust in‚ĀĘ Marine Environments
African dust‚Äć is not just a nuisance; ‚Ā£it plays a crucial role‚Äć in our planet’s ecosystems. Originating ‚Äćfrom the Sahara Desert, these‚Ā§ fine ‚ÄĆparticles travel thousands of miles across the Atlantic Ocean, directly impacting sea surface conditions and nutrient availability.
What is Phytoplankton?
Phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that inhabit the upper layers of the oceans, lakes, and other bodies of water. As ‚ĀĘprimary producers,‚Äć they are fundamental to the‚Ā£ aquatic food ‚Ā§web, forming the base of all ‚ĀĘmarine food‚ĀĘ chains.
The‚Ā£ Importance‚Ā§ of Phytoplankton Blooms
- Oxygen Production: Phytoplankton ‚Äčcontribute to about‚Ā£ 50% ‚ÄĆof the Earth’s ‚ÄĆoxygen supply.
- Carbon Sequestration: They ‚Ā£play a vital role in the ‚ÄĆglobal‚Ā§ carbon cycle,‚Äć absorbing carbon dioxide as they grow.
- Biodiversity Support: Phytoplankton blooms support diverse marine life, from fish to larger mammals.
The Mechanism ‚ÄčBehind the Dust-Phytoplankton Connection
The relationship between African dust and phytoplankton blooms is a prime example of nature’s interconnectedness. When dust particles accumulate in ocean waters,‚Ā§ they bring with them vital nutrients, particularly iron, phosphorous, and nitrogen. Below are‚Ā§ specific ways in ‚ĀĘwhich this process occurs:
1. Nutrient Enrichment
The primary mechanism is‚Äć nutrient enrichment. African dust ‚Ā§contains essential minerals that,‚ÄĆ when deposited into ocean waters, stimulate precise phytoplankton growth.‚ĀĘ
- Iron: A‚Ā£ crucial micronutrient, iron stimulates phytoplankton productivity.
- Phosphorous ‚Ā§and‚Ā£ Nitrogen: ‚Ā£These macronutrients help in cellular growth and‚Äč reproduction.
2. Ocean Circulation and Weather Patterns
The path of African dust is influenced by specific weather patterns and ocean currents, which play a significant role in determining where and when phytoplankton blooms occur.
Case Studies in Phytoplankton Blooms
Multiple research studies illustrate the crucial link between African dust ‚Ā£and‚Ā§ phytoplankton growth.‚ĀĘ
Case Study: The 2015 ‚ÄčBloom ‚ĀĘin the Gulf of Mexico
In 2015,‚Äć researchers noted a substantial phytoplankton bloom in the Gulf of Mexico‚ĀĘ following a profuse dust event from the Sahara. ‚ÄćSatellite imagery revealed:
| Month | Dust Concentration (¬Ķg/m¬≥) | Phytoplankton Biomass (mg/m¬≥) |
|---|---|---|
| June | 500 | 20 |
| July | 600 | 45 |
| August | 450 | 15 |
This‚ÄĆ bloom not ‚Äćonly contributed to ‚Äćthe region’s ecology but‚Ā£ also provided‚Ā£ insights into how oceanic systems respond to external inputs.
The Benefits of Phytoplankton Blooms
Phytoplankton blooms are beneficial beyond ecological‚Ā£ systems; they also provide economic‚Äč and ‚Äćenvironmental ‚Ā£support.
Ecological Benefits
- Feeding Fish Populations: Increased ‚Äćphytoplankton leads to‚Ā§ healthier‚Ā£ marine ecosystems, supporting larger‚Ā£ fish and marine mammal populations.
- Biodiversity: ‚Ā£They help‚Ā£ maintain marine biodiversity, ‚ĀĘa critical factor for‚Äć sustainable‚Äč oceans.
Economic Advantages
- Fisheries: Healthy phytoplankton populations can lead to abundant‚Ā£ fish catches, supporting local economies.
- Tourism: Areas with vibrant marine life tend to ‚Ā£attract tourists, bolstering local economies.
Carbon Capture
Phytoplankton contributes significantly to‚ĀĘ carbon capture‚Äć through photosynthesis, which can help mitigate climate‚Äć change.
Practical Tips to Study‚Äć Phytoplankton Trends
For educators and ‚ĀĘresearchers looking‚ÄĆ to delve into the ‚Ā£effects of ‚ÄćAfrican dust‚Ā§ and phytoplankton:
- Utilize‚Ā£ Satellite Data: Access data from‚Ā§ NASA’s MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) to study phytoplankton biomass.
- Field Studies: Engage in field studies to collect water samples and ‚ĀĘmeasure nutrient levels in various oceanic regions.
- Collaborate with ‚Ā§Local Institutions: Partner with marine research organizations for shared‚Äč insights and data collection.
First-Hand‚ÄĆ Experiences: The Researcher’s Perspective
Dr. Lisa Thompson, ‚ĀĘa‚Ā§ marine biologist, recalls‚ÄĆ her experiences studying the impact of African dust‚Äć on the Caribbean Sea:
>“Witnessing a vibrant phytoplankton bloom ‚Ā§after a dust storm was awe-inspiring. The sheer ‚Äćabundance of life it supported highlighted how intricate our ecosystems ‚Äćare and how they respond to changes in ‚ĀĘtheir environment.”
This firsthand experience illustrates the deep connection‚Ā§ between terrestrial systems and oceanic health.
Conclusion
The relationship‚ÄĆ between African dust and phytoplankton blooms showcases nature’s remarkable chain reactions. ‚Ā§Understanding how these elements‚ÄĆ interact ‚Ā£not only broadens our scientific knowledge but also emphasizes the importance of protecting both land and‚ĀĘ sea ecosystems for ‚Äća‚Ā§ healthier planet.
A‚Ā£ Dual‚Äč Role: Benefits vs Risks
Dust serves a crucial‚Ā§ purpose in natural‚Äč ecosystems‚ÄĒproviding essential nutrients beneficial for‚Ā£ plant growth and fostering planktonic ‚ÄĆlife which ‚Ā§supports‚Ā§ entire aquatic food webs. However, excessive‚Ā£ quantity can result in severe air pollution‚Äć adversely‚ĀĘ affecting human health while diminishing visibility conditions‚ÄĒa complex balancing‚ÄĆ act that underscores both its advantages and drawbacks ‚Äćwithin environmental systems.
Future Research‚ĀĘ into Dust’s Ecological Impact
The ‚Ā£work conducted by Dr.‚Äč Gittings’ team represents progressive strides toward comprehending how ‚Ā£various factors ‚Äčintricately‚Äč associate ‚Ā§with climate change affect our oceans through phenomena like airborne particulates‚ÄĒand necessitates further inquiry‚Ā§ into ‚Ā£how such ‚ÄĆdynamics could ‚ĀĘpotentially reshape ecological balances going forward.
More collaborative global‚Äč efforts merging enhanced satellite surveillance capabilities with advanced climatic‚ÄĆ models‚Ā§ are essential steps required for deciphering these‚Äč critical‚Ā£ complexities regarding Earth‚Äôs atmospheric‚Äć interactions moving ahead into an‚Ā£ uncertain future shaped increasingly by environmental changes driven primarily through‚ĀĘ human activity over ‚Ā£time.
Understanding Our Planetary ‚Ā£Interconnectivity
Marie-Helene Rio at ESA underlined ‚ÄĆjust ‚ĀĘhow essential oceans are‚ÄĒthey cover approximately ‚Äćtwo-thirds of Earth’s surface‚ÄĒfunctioning as key players within‚Ā£ our‚Ā£ ecosystems‚Äô overall well-being.
‚Ā£
‚ÄúLeveraging‚Äč access to‚Äč comprehensive satellite data‚Äć allowed ‚Ā£us great clarity when‚ÄĆ mapping out both‚Äć spatial ‚ÄĆscales tied directly back towards identifying contributing sources creating these blooms,‚ÄĚ noted Dr.Gittings about their findings.
This investigation serves as poignant reminder about‚ĀĘ interconnectedness we ‚Äćall ‚Ā£share globally; even‚Äć minuscule elements can lead towards monumental implications when examined holistically.Establishing awareness surrounding‚Äć such relationships ‚ĀĘbetween disparate systems ‚ÄĆwill‚Äć be‚Ā£ paramount‚Äć if humanity hopes maintain balance amid ongoing shifts sustained throughout‚Äč environments‚Äč worldwide today.
For those interested in similar‚ĀĘ topics‚Ā£ or wishing updates‚Ā£ on recent studies‚Ā£ subscribe below! Also explore EarthSnap‚ÄĒa‚Äč free app designed ‚Ā£by Eric Ralls along with additional content‚ĀĘ available at ‚ĀĘEarth.com!